
Script Component Reference

Overview
The Script component has many uses; it could be used to execute a script that prompts a response from a client before the payload is processed, or to enrich data on a web page requested by a client. The Script component provides developers with the facilities to integrate custom scripts into a flow that support a JSR-223 compliant script engine. When using a Script component, the developer must select a script engine that is compatible with the language used to create the custom script. This flexibility enables scripts to be written in Groovy, JavaScript, Python, or Ruby. As an example, you can write a custom script for an application (using supported languages), save it in a separate file and then configure the Script component to reference the file. Or, after placing the Script component on the Studio canvas you can type in the script through the Script Pattern Properties pane.
Script also allows the developer to configure interceptors and alter the values or references of particular properties in a script. Interceptors are configured to provide additional services to a message as it flows through a component. For example, a developer can configure an interceptor to execute scheduling or logging of a particular event while a message is being processed. The Script component also includes a custom interceptor which allows you to configure settings for Spring elements. Use the Advanced tab to access Script Properties, then define the value and reference for a particular property in the script.
When using Script, typing-in or appending a script to the component is the only configuration required. Remember, JavaScript is the default scripting engine, use the drop-down box to select another engine.
Configuration
If you add a Script component to an endpoint, such as a request-response HTTP endpoint, Studio generates a Script request-response component, as shown below.
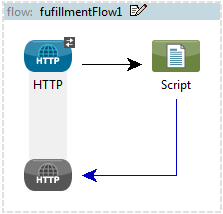
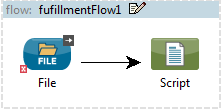
If you add the Script component to a one-way endpoint, such as a File endpoint, then Studio generates a Script one-way component, as shown below.
General Tab
To configure the Script component, from the Message Flow canvas double-click the Script icon to open the Pattern Properties pane. Use the General tab to specify the file location of the script or simply type in the script on the script text window.
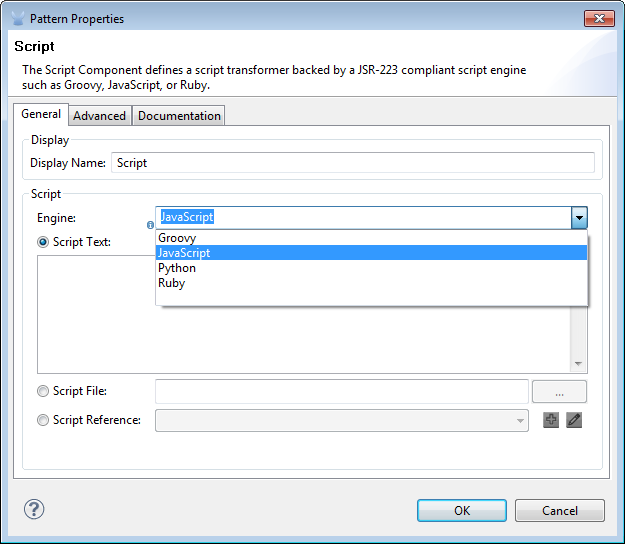
| Panel | Description |
|---|---|
Display |
Defaults to the generic component name. Change the Display Name, which must be alpha-numeric, to reflect the component’s specific role, i.e., |
Script |
From the Engine property pull-down list select a scripting engine. Scripting engine choices are: JavaScript, Groovy, Python, and Ruby. The default scripting engine is JavaScript. After choosing the scripting engine, select one of the following ways to reference the script. |
Advanced Tab
Use the Advanced tab to optionally configure interceptors and (depending on the interceptor) enter Spring values. You also have the option to specify script properties, which are key/value pairs used to alter or change properties in the script.
+ image::scriptpropadv2.png[ScriptPropAdv2]
+
| Panel | Description |
|---|---|
Interceptors Management |
Interceptors enable the developer to provide additional services to the component such as the ability to log transactions and the ability to log the time for each transaction. Use the Add Custom Interceptor to create a custom interceptor that can reference Spring objects. The Interceptor Stack enables you to bundle multiple interceptors. Use the Interceptor Stack to apply multiple interceptors on a Groovy component. The interceptors will be applied in the order defined in the stack. |
Script Properties |
Configure these parameters to define the attribute keys and their associated values. This enables the script component to quickly look up a value associated with a key. |
Documentation Tab
The Documentation tab lets you add optional descriptive documentation for the Script component. Each component has a Documentation tab and optional Description field.
| Panel | Description |
|---|---|
Documentation |
Enter all relevant information regarding this Script component. This information is displayed in Studio when you hover over the component icon on the Message Flow canvas. |
Mule ESB Reference
For more information see the Mule ESB page Scripting Module.



