Studio Visual Editor
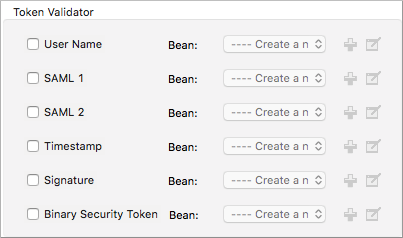
You configure a security token to identify API callers using a key-value pair where the value is a CXF WSS4J security-configuration text string or a value reference:
-
The string value is one of the following constants: ** WSConstants, a class to define the kind of access the server allows
-
WSHandlerConstants, a class to specify the names, actions, and other strings for data deployment of the WSS handler
-
-
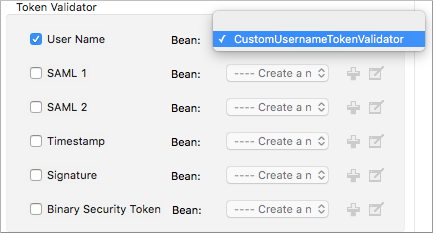
The bean Value Reference is the name of the bean that the key references. For example, when the key is
passwordCallbackRef, enter the name of the bean in the Value Reference field.
To configure the CXF component, you enter a string value UsernameToken in the value field under Add Configuration Element. In XML, this step mirrors the addition of a key-value pair inside the ws-config child element of a ws-security element. By adding configuration elements to your SOAP component, you are creating a map of key-value pairs that correspond to the CXF WSS4J security-configuration text strings.
To secure a SOAP API:
-
Open the properties editor, then click the Security tab.
-
Click
 in Add Configuration Element to create a new key-value pair.
in Add Configuration Element to create a new key-value pair.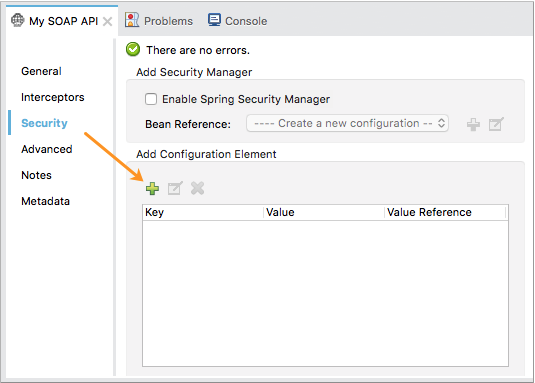
The
cxf:propertydefault key name appears. -
In the Key field, replace the default key with a name, for example
action. -
Enter a value, for example
UsernameToken, in the Value field.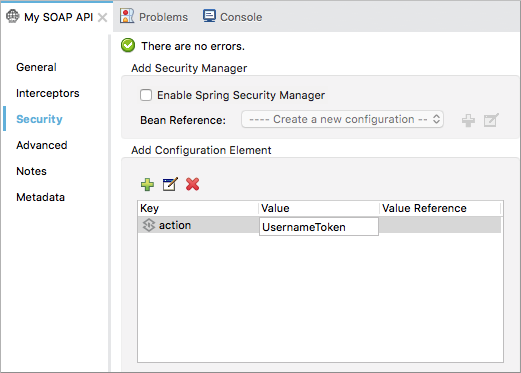
-
Click Finish to save the key-value pair.
-
Repeat these steps to add as many
ws-securityconfigurations as you need, then click OK.
Studio Visual Editor or Standalone
-
To your CXF element (i.e. SOAP component), add a child element for
cxf:ws-security. -
Within the
cxf:ws-securitychild element, add a child element forcxf:ws-config. -
Within the
cxf:ws-configchild element, add a child element forcxf:property. -
Add two attributes to the cxf:property child element according to the table below. Be sure to enter either a
value `OR a `value-ref; the two are mutually exclusive.Attribute
Description
key
Specify a name for the property.
value
Specify a WS Constant (a class to define the kind of access the server allows) or a WSHandlerConstant (a class to specify the names, actions, and other strings for data deployment of the WSS handler). For example, enter
UsernameTokenin the value field.value- ref
Specify the bean that the key must reference. When the key must reference a bean (for instance, when the key is
passwordCallbackRef), specify the name of the bean as the value-ref. -
Repeat the preceding step to add as many WS-security configurations as you want to your API. Refer to the following sample code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule xmlns:cxf="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/cxf"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/cxf http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/cxf/current/mule-cxf.xsd">
<http:listener-config name="listener-config" host="localhost" port="8081"/>
<flow name="Creation1Flow1" doc:name="Creation1Flow1">
<http:listener config-ref="listener-config" path="/" doc:name="HTTP Connector"/>
<cxf:jaxws-service doc:name="SOAP">
<cxf:ws-security>
<cxf:ws-config>
<cxf:property key="action" value="UsernameToken"/>
</cxf:ws-config>
</cxf:ws-security>
</cxf:jaxws-service>
</flow>